Waterfall Model (Theory)
1. Compare
Waterfall Model vs. V Model (Difference & Similarities)
Waterfall Model
The
waterfall model is a breakdown of project activities into linear sequential
phases, where each phase depends on the deliverables of the previous one and
corresponds to a specialization of tasks. It is also called a classical model
used in system development life cycle to create a system with a linear and
sequential approach. It is termed as waterfall because the model develops
systematically from one phase to another in a downward way. All these phases
are cascaded to each other in which progress is seen as flowing steadily
downwards (like a waterfall) through the phases. The next phase is started only
after the defined set of goals are achieved for previous phase and it is signed
off, so the name "Waterfall Model". Let’s take a look at an example
of a software engineering project plan using a waterfall model. In this
example, we’ve scoped out tasks for adding a new app feature. When one task or
milestone is complete, the next one begins. For example, deployment can’t
happen until the Testing + Revision phase wraps. The following sequential
phases are performed in waterfall model to complete any task or project.
Figure 1: Waterfall Model
1.
Requirement Analysis
The
first phase in waterfall model which involves the understanding of what needs
to be design and what is it function or purpose of the project is identified. Here,
the specifications of the input and output are well documented, studied and
marked which helps to understand the clear vision of the project for the future
reference.
2.
System Design
The
requirement specifications from the first phase are studied in this phase and
system design is prepared. System Design helps in specifying hardware and
system requirements and also helps in defining overall system architecture. The
software code to be written in the next stage is created now.
3.
Implementation
With
inputs from the system design, the system is first developed in small programs
called units, which are integrated in the next phase. Each unit is developed
and tested for its functionality, which is referred to as Unit Testing.
4.
Testing & Integration
All
the units developed in the implementation phase are integrated into a system
after testing of each unit. The software designed, needs to go through constant
software testing to find out if there are any flaws or errors. Testing is done
so that the client does not face any problem during the installation of the
software. Because of every time interaction with the clients/users, the
software will be good in quality in a quantitative way.
5.
Deployment
Once
the functional and non-functional testing is done; the product is deployed in
the customer environment or released into the market. First, we can deployed
the different version of the product to the public for testing purpose. After received
the good feedback, then we could deploy the full product to the market for
publicly use.
6.
Maintenance
After
deployment of the product into the market, there are some issues which would
come up in the client environment. Such changes occur either from
customer-initiated demands for improvement, or from vulnerabilities found
during the system's live use. To fix those issues, patches are released. Also
to enhance the product some better versions are released. That’s why, maintenance
is done to deliver these changes in the customer environment.
V.
Model
The
V-model is a type of SDLC model where process executes in a sequential manner
in V-shape. It is also known as Verification and Validation model. It is based
on the association of a testing phase for each corresponding development stage.
Development of each step directly associated with the testing phase. The next
phase starts only after completion of the previous phase i.e. for each
development activity, there is a testing activity corresponding to it.
Here
it corresponds the two main factors in this model. One is Verification, which
involves static analysis technique (review) done without executing code. It is
the process of evaluation of the product development phase to find whether
specified requirements meet.
And another is Validation, which refers to the dynamic analysis technique (functional, non-functional), testing done by executing code. Validation is the process to evaluate the software after the completion of the development phase to determine whether software meets the customer expectations and requirements.
So V-Model contains Verification phases on one side of the Validation phases on the other side. Verification and Validation phases are joined by coding phase in V-shape. Thus it is called V-Model.
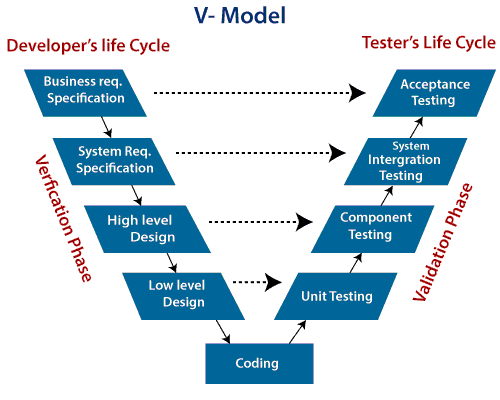
Figure 2: V-Model
1. Business
Requirement Analysis
This is the
first phase in the development cycle where the product requirements are
understood from the customer’s perspective. This phase involves detailed
communication with the customer to understand his expectations and exact
requirement. This is a very important activity and needs to be managed well, as
most of the customers are not sure about what exactly they need. So, this stage
is also known as main Requirement Gathering stage.
2. System
Requirement Specification
Once you
have the clear and detailed product requirements, it is time to prepare the
complete system requirement. The system requirement specification will have the
understanding and detailing the complete hardware and communication setup for
the product under development. The system test plan is also developed based on this
phase.
3. High
Level Design (Architectural Design)
Architectural
specifications are understood and designed in this phase. Usually more than one
technical approach is proposed and based on the technical and financial
feasibility the final decision is taken. System design is broken down further
into different modules taking up different functionalities. The data transfer
and communication between the internal modules and with the outside world
(other systems) is clearly understood.
4. Low Level
Design (Module Design)
In this phase the system breaks down
into small modules. The detailed design of modules is specified, that’s why it
called low level design. It is important that the design is compatible with the
other modules in the system architecture and the other external systems. Unit
tests which helps to eliminate maximum faults and errors at the early stage in
the system, can be designed at this stage based on the internal module designs.
Validation
Phases
The different validation phases in
the V-Model are explained in details below:-
1.
Unit Testing
Unit tests
designed in the module design phase are executed on the code during this
validation phase. Unit testing is the testing at code level and helps eliminate
bugs at an early stage, though all defects cannot be uncovered by unit testing.
2.
Integration Testing
After
completion of unit testing Integration testing is performed. In integration
testing, the modules are integrated and the system is tested. Integration
testing is performed on the Architecture design. This test verifies the
communication of modules among themselves.
3. System Testing
System
testing is directly associated with the system design phase. System tests check
the entire system functionality and the communication of the system under
development with external systems. Most of the software and hardware
compatibility issues can be uncovered during this system test execution. It
also tests the functional and non-functional requirements of the developed
application.
4.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
UAT is associated with the business
requirement analysis phase and involves testing the product in user environment
that resembles the production environment. UAT verifies that the delivered
system meets user’s requirement and system is ready for use in real world.
Comparison between Waterfall & V.
Model
|
Basis |
Waterfall Model |
V. Model |
|
Cost |
The cost of waterfall
model is low. |
This model is expensive. |
|
Simplicity |
It is simple and straight
forward model. |
It is little hard to
implement & understand than waterfall. |
|
Flexibility |
Flexibility of this model
is Rigid. |
Little more flexible than
waterfall. |
|
Process |
It is a sequential Model
Process. |
It is also a sequential
Model Process. |
|
Way of execution |
Steps move in a linear
continuous way. |
Steps move in simultaneous
process. |
|
Re-usability |
Re-usability is limited. |
Can re-use for some extent
to. |
|
User Involvement |
Only in the beginning. |
Only in the beginning too. |
|
Testing |
Testing only performs
after the development. |
Testing performs and
planning in every phase. |
|
Durability |
Guarantee of success rate
is low. |
Guarantee of success rate
is high. |
|
Debugging rate |
Software made using
Waterfall model, the number of defects are less in comparison of software
made using V-model. |
Software made using
V-model, the number of defects are greater in comparison of software made
using Waterfall model. |
|
Requirement Specification |
Requirement Specification
is necessary in the beginning. |
Requirement specification
is also necessary in the beginning. |
|
Used Criteria |
Less used nowadays. |
Widely Used than the
waterfall model. |
Bibliography
TeamGantt. https://teamgantt.com. [Online]
ToolsQa. https://www.toolsqa.com.
[Online]
Tutorials Point. https://www.tutorialpoint.com.
[Online]
WiKiPedia. https://www.wikipedia.org.
[Online]


Comments
Post a Comment